Have you ever received your salary arrears and felt confused about the high tax deduction? You’re not alone! Many salaried employees face this issue every year when arrears are paid for previous financial years. Thankfully, the Income Tax Act’s Section 89(1) provides a simple solution — and with Form 10E, you can claim tax relief smartly and legally.
Think of it as a “time machine for taxes” — you can adjust the extra tax you pay today for income that belonged to the past. Let’s dive deep into understanding how the Salary Arrears Relief Calculator U/s 89(1) and Form 10E help you manage your tax smartly from FY 2000-01 to FY 2025-26.
Table of Contents
| Sr# | Headings |
| 1 | What is Section 89(1) and Why Does It Exist? |
| 2 | Understanding Form 10E and Its Purpose |
| 3 | When Should You Use Form 10E? |
| 4 | Step-by-Step Guide to Filling Form 10E Online |
| 5 | What Are Salary Arrears and How Do They Impact Tax? |
| 6 | Detailed Example: Calculating Relief U/s 89(1) |
| 7 | Salary Arrears Relief Calculator: How It Simplifies Your Work |
| 8 | Benefits of Using Excel-Based Automatic Calculator |
| 9 | How to Download and Use the Calculator for FY 2000-01 to 2025-26 |
| 10 | Common Mistakes While Submitting Form 10E |
| 11 | Key Points to Remember Before Claiming Relief |
| 12 | Difference Between Old and New Tax Regime in Claiming Relief |
| 13 | Practical Tips for Salaried Employees |
| 14 | Importance of Accurate Data in Form 10E |
| 15 | Final Thoughts on Smart Tax Management |
| 16 | FAQs |
1. What is Section 89(1) and Why Does It Exist?
Section 89(1) is a lifesaver for those who receive salary arrears, gratuity, or pension for earlier years. It ensures that you don’t pay extra tax just because your employer paid you late.
For instance, imagine you earned money for FY 2019-20 but received it in FY 2024-25. The tax rates might have changed, and the lump sum payment could push you into a higher tax bracket. Section 89(1) helps balance this unfair situation by spreading the income over the years it belonged to.
2. Understanding Form 10E and Its Purpose
Form 10E is the official document that allows you to claim this tax relief. Without submitting it, the Income Tax Department will reject your claim, even if you’re eligible under Section 89(1).
It’s like showing proof — “Yes, this income belongs to previous years, and here’s how I’m calculating the relief.” The form is submitted online through the Income Tax e-filing portal before filing your return.
3. When Should You Use Form 10E?
You should file Form 10E whenever you receive:
- Salary arrears or advance salary
- Gratuity for past service
- Pension or commuted pension
- Family pension arrears
Basically, any lump-sum payment that affects your taxable income for a previous year qualifies for relief under Section 89(1).
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Filling Form 10E Online
Follow these steps carefully to avoid errors:
- Login to the Income Tax e-filing portal.
- Go to ‘e-File’ → ‘Income Tax Forms’ → ‘File Income Tax Forms’.
- Choose Form 10E under ‘Persons with Salary Arrears’.
- Select the Assessment Year relevant to the current filing.
- Enter your salary details, arrear amount, and year-wise breakup.
- Save the draft and review all entries.
- Submit the form before filing your ITR.
Remember, you don’t need to attach Form 10E with your ITR — just file it online beforehand.
5. What Are Salary Arrears and How Do They Impact Tax?
Salary arrears mean payments due for previous financial years but received in the current year. When you receive these arrears, your total income for the year increases, possibly pushing you into a higher tax slab.
That’s where Form 10E comes in — it helps you recalculate the tax as if the arrears were received in the original years, giving you a fair tax relief.
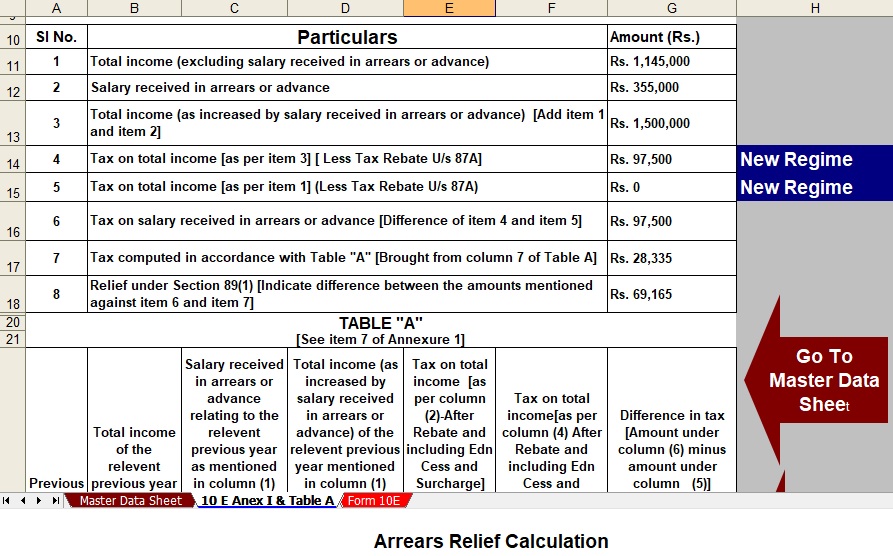
6. Detailed Example: Calculating Relief U/s 89(1)
Let’s break it down with an example:
Suppose Mr. A received ₹1,20,000 as arrears in FY 2024-25 related to FY 2020-21.
- Calculate tax on total income, including arrears in FY 2024-25.
- Calculate tax on total income excluding arrears in FY 2024-25.
- The difference = Extra tax paid due to arrears.
- Calculate tax for FY 2020-21 with arrears.
- Calculate tax for FY 2020-21 without arrears.
- The difference = Tax payable if arrears were paid then.
- Finally, Relief = Step 3 – Step 6.
This ensures you pay the right amount of tax, not more.
7. Salary Arrears Relief Calculator: How It Simplifies Your Work
Manual calculation can be complex and time-consuming. That’s why many prefer the Automatic Salary Arrears Relief Calculator in Excel, which instantly computes relief U/s 89(1) with minimal input.
You just enter your income, arrear amount, and tax slabs — and the calculator does all the math for you accurately.
8. Benefits of Using an Excel-Based Automatic Calculator
The Excel-based Form 10E Relief Calculator offers:
- Accuracy: No manual errors.
- Speed: Instant results.
- Ease: Simple input fields and automatic formulae.
- Comprehensive Data: Covers FY 2000-01 to FY 2025-26.
- Comparison: Helps you visualise year-wise relief clearly.
It’s like having a digital tax consultant right in your spreadsheet.
9. How to Download and Use the Calculator for FY 2000-01 to 2025-26
- Download the Excel-based tool from a trusted source.
- Open the file and enable macros if prompted.
- Enter your basic salary, arrears, taxable income, and assessment years.
- The calculator automatically applies tax slabs for each year.
- It displays your relief amount U/s 89(1)
This calculator helps you save both time and money while ensuring compliance with Form 10E requirements.
10. Common Mistakes While Submitting Form 10E
Many taxpayers lose their relief due to small mistakes, such as:
- Forgetting to file Form 10E before ITR
- Entering the wrong financial years.
- Not matching the arrears figures with Form 16.
- Using incorrect tax slabs for previous years.
Double-check every detail before submitting to avoid rejection.
11. Key Points to Remember Before Claiming Relief
- Always file Form 10E
- Keep proof of arrears (like pay slips or HR letters).
- Use the correct assessment year while filing.
- Don’t submit physical copies — it’s entirely digital now.
- Keep a copy of the acknowledgement for your records.
12. Difference Between Old and New Tax Regime in Claiming Relief
Interestingly, the New Tax Regime (under Section 115BAC) does not affect your eligibility for relief under Section 89(1). You can still claim it using Form 10E, regardless of the regime chosen.
However, most employees prefer the Old Regime while claiming arrear relief since it allows deductions like 80C, 80D, and HRA benefits.
13. Practical Tips for Salaried Employees
- Maintain a year-wise salary record.
- Use Excel calculators for quick computation.
- Cross-check tax slabs for relevant years on the IT Department website.
- If in doubt, consult a tax professional.
- Always submit Form 10E before filing your return.
These small steps ensure smooth processing and timely tax refunds.
14. Importance of Accurate Data in Form 10E
Accuracy is crucial. Even a small mismatch between Form 10E and Form 16 can trigger scrutiny. Always verify:
- Your PAN and personal details.
- The year of arrears.
- Gross income for each relevant year.
- The tax calculation from the Excel sheet.
A simple error can delay your refund or cause notice from the IT Department.
15. Final Thoughts on Smart Tax Management
Understanding and using Form 10E isn’t just about tax saving — it’s about financial discipline. By correctly claiming relief under Section 89(1), you ensure fairness in taxation and keep your finances balanced.
With the help of the Automatic Salary Arrears Relief Calculator, managing arrears from FY 2000-01 to FY 2025-26 becomes effortless and transparent.
FAQs
- What is Form 10E used for?
Form 10E is used to claim relief under Section 89(1) for salary arrears, gratuity, or pension received for previous financial years. - Is it mandatory to file Form 10E before filing ITR?
Yes. You must file Form 10E online before submitting your Income Tax Return; otherwise, your relief claim will be rejected. - Can I file Form 10E offline?
No. Form 10E must be filed online through the Income Tax e-filing portal. - What happens if I forget to submit Form 10E?
Your tax relief claim under Section 89(1) will be denied, and your refund (if any) will be delayed. - Can I claim arrear relief under both old and new regimes?
Yes, relief under Section 89(1) is available under both tax regimes; however, deductions differ under each.
✅ In Summary:
By using the Salary Arrears Relief Calculator U/s 89(1) and filing Form 10E correctly, you can reduce unnecessary tax burdens and ensure fairness across financial years — making smart tax planning a simple reality.
Free Download Automatic Income Arrears Relief Calculator with Form 10E for F.Y.2025-26