Introduction
When it’s time to file your income tax for F.Y. 2025–26, one question naturally arises — Should you go with the Old Tax Regime or the New Tax Regime?
Each system has its own strengths, weaknesses, and levels of flexibility. With the 2025 Budget updates, understanding which option fits your income level and lifestyle can make a big difference to your savings.
To simplify things, you can use an Automatic Income Tax Preparation Software (All-in-One) in Excel — especially designed for Non-Government Employees. This smart tool compares both regimes instantly and helps you calculate your tax accurately and efficiently.
Let’s explore both systems in detail and uncover which one helps you save the most this financial year.
Table of Contents
| Sr# | Headings |
| 1 | Understanding the Old Tax Regime |
| 2 | Understanding the New Tax Regime |
| 3 | Key Differences Between Old and New Regimes |
| 4 | Benefits of the Old Tax Regime |
| 5 | Benefits of the New Tax Regime |
| 6 | Which Regime Offers More Savings? |
| 7 | Impact of the 2025 Budget on Tax Regimes |
| 8 | Deductions and Exemptions under the Old Regime |
| 9 | Simplified Slab Structure in the New Regime |
| 10 | Choosing the Right Regime for Salaried Employees |
| 11 | Role of Excel-Based Income Tax Calculator |
| 12 | Step-by-Step Guide: Using Automatic Tax Preparation Software |
| 13 | Common Mistakes to Avoid While Filing Taxes |
| 14 | Practical Example: Comparing Two Scenarios |
| 15 | Conclusion – Which Regime is Better for You? |
| 16 | FAQs |
Choosing between the Old Tax Regime and the New Tax Regime often feels overwhelming, especially when you want to save more and plan wisely. Because the Union Budget 2025 introduced multiple changes, you must clearly understand how both tax systems influence your income, investments, and financial security. So, in this active-voice, easy-to-read guide, I explain each regime in detail, compare their differences, and help you decide confidently.
Table of Contents
| Sr# | Headings |
| 1 | Understanding the Old Tax Regime |
| 2 | Key Features of the Old Regime |
| 3 | Understanding the New Tax Regime |
| 4 | Key Features of the New Regime |
| 5 | Major Differences Between Both Regimes |
| 6 | Benefits of the Old Tax Regime |
| 7 | Benefits of the New Tax Regime |
| 8 | Impact of Union Budget 2025 |
| 9 | Popular Deductions Under the Old Regime |
| 10 | New Regime Tax Slabs for FY 2025–26 |
| 11 | How to Choose the Right Regime |
| 12 | Role of Excel-Based Tax Calculators |
| 13 | Step-by-Step Guide to Using Tax Software |
| 14 | Common Tax Filing Mistakes to Avoid |
| 15 | Practical Example: Old vs New Tax Regime |
| 16 | Conclusion |
| 17 | FAQs |
1. Understanding the Old Tax Regime
The Old Tax Regime encourages you to plan your finances actively. It offers several deductions and exemptions that directly reduce your taxable income. Because it rewards disciplined investment behaviour, you gain more control over your tax planning.
2. Key Features of the Old Regime
When you choose the Old Regime, you enjoy multiple ways to lower your tax burden. You claim deductions, submit investment proofs, and reduce your taxable income effectively. Although this regime demands paperwork, it empowers you with strategic control.
Important Features Include:
- Over 70 deductions and exemptions
- Lower taxable income through investments
- Benefits under Section 80C, 80D, 80CCD(1B), HRA, LTA
- Ideal for disciplined investors and planners
Because these options significantly reduce taxable income, the Old Regime suits people who prefer structure and long-term planning.
3. Understanding the New Tax Regime
The New Tax Regime simplifies taxation. Instead of offering exemptions or deductions, it provides lower tax rates across slabs. Since the system requires no proofs or paperwork, taxpayers can file returns quickly.
4. Key Features of the New Regime
The New Regime removes complexity by offering a clean, easy-to-follow structure.
Key Features Include:
- Lower tax rates
- No need to invest to save tax
- Minimal documentation
- Higher liquidity and take-home salary
- Default regime from FY 2025–26
In short, the New Regime helps modern earners who want freedom from documentation and strict investment commitments.
5. Major Differences Between Both Regimes
To help you choose wisely, let’s compare them:
| Aspect | Old Regime | New Regime |
| Exemptions/Deductions | Many | Very Few |
| Tax Rates | Higher | Lower |
| Documentation | Required | Not Required |
| Flexibility | High for investors | High for simplicity seekers |
| Ideal For | Planners | Minimalists |
Because of these differences, the Old Regime supports long-term tax planning, whereas the New Regime supports ease and convenience.
6. Benefits of the Old Tax Regime
The Old Regime continues to help taxpayers who invest regularly.
Top Advantages Include:
- Section 80C deduction up to ₹1.5 lakh
- Section 80D health insurance tax savings
- Section 80CCD(1B) NPS deduction up to ₹50,000
- HRA exemption for rented homes
- LTA exemption for travel
- Home loan interest deduction (Section 24b) up to ₹2 lakh
These deductions, when combined, significantly reduce taxable income.
7. Benefits of the New Tax Regime
The New Regime promotes stress-free filing and minimal compliance.
Most Notable Benefits Include:
- Reduced tax rates
- No documentation required
- Higher in-hand salary
- Default regime from FY 2025–26
- Ideal for those with fewer investments
Many salaried individuals prefer this because it simplifies life while still saving tax.
8. Impact of Union Budget 2025
Budget 2025 introduced impactful updates:
- Higher basic exemption limit
- Standard deduction available in both regimes
- Enhanced Section 87A rebate
- Improved fairness and simplicity
These changes make the New Regime more attractive while keeping the Old Regime relevant.
9. Popular Deductions Under the Old Regime
If you choose the Old Regime, you can claim several deductions:
Most Used Deductions:
- Section 80C: PPF, ELSS, EPF, NSC, LIC
- Section 80D: Medical insurance
- Section 24(b): Home loan interest
- HRA & LTA: Rent and travel
These deductions can reduce your taxable income significantly, allowing you to save more.
10. New Regime Tax Slabs for FY 2025–26
Under the New Regime, the tax slabs are:
| Income Range (₹) | Tax Rate |
| 0 – 3,00,000 | Nil |
| 3,00,001 – 6,00,000 | 5% |
| 6,00,001 – 9,00,000 | 10% |
| 9,00,001 – 12,00,000 | 15% |
| 12,00,001 – 15,00,000 | 20% |
| Above 15,00,000 | 30% |
This transparent structure helps you decide quickly.
11. How to Choose the Right Regime
Because every taxpayer has a different financial pattern, you must evaluate your choices carefully.
Ask yourself these questions:
- Do I claim many deductions?
If yes → Choose Old Regime. - Do I want simplicity and a higher in-hand salary?
If yes → Choose New Regime. - Do I invest regularly to save tax?
If yes → Old Regime supports your style. - Do I avoid documentation and proofs?
If yes → New Regime suits you.
12. Role of Excel-Based Tax Calculators
An Automatic Excel Income Tax Calculator helps you:
- Compare both regimes instantly
- Avoid calculation errors
- Calculate taxable income accurately
- Get quick results
- Plan better
It acts like your personal tax assistant—available anytime.
13. Step-by-Step Guide to Using Tax Software
Follow these steps:
- Download the Excel Utility for FY 2025–26
- Enter salary components (Basic Pay, HRA, Allowances)
- Select Old or New Regime
- Add deductions (Only for Old Regime)
- Let the software calculate tax automatically
- Compare both results
- Choose the regime with maximum savings
In just a few minutes, you get accurate tax results.
14. Common Tax Filing Mistakes to Avoid
Avoid these common errors:
- Forgetting to select your tax regime
- Submitting incorrect values
- Missing Form 10IEA while switching regimes
- Ignoring the Section 87A rebate
- Entering wrong HRA or deduction amounts
By avoiding these mistakes, you prevent penalties and notices.
15. Practical Example: Old vs New Tax Regime
Let’s take an example:
Ravi’s Income: ₹12,00,000 annually
Under the Old Regime:
Deductions = ₹2,00,000
Taxable Income = ₹10,00,000
Under New Regime:
No deductions
Taxable Income = ₹12,00,000 (but taxed under lower slabs)
Using an Excel calculator, Ravi compares both and chooses the better option instantly.
Conclusion
Choosing between the Old vs New Tax Regime depends on your financial habits. If you love investing and enjoy structured planning, choose the Old Regime. If you want simplicity, higher liquidity, and stress-free filing, choose the New Regime. Using an Automatic Excel Tax Calculator helps you compare both instantly and choose wisely.
FAQs
1. Which regime offers more tax savings for most people?
If you claim many deductions, the Old Regime usually saves more. If not, the New Regime offers better take-home income.
2. Can I switch between tax regimes every year?
Yes, salaried employees can switch annually, but business owners must follow restrictions.
3. Is Form 10IEA mandatory for choosing the New Regime?
Yes, if you want to switch from Old to New Regime, you must file Form 10IEA before the deadline.
4. Does the New Tax Regime allow any deductions?
It offers very few deductions, but it allows standard deduction and employer NPS contributions.
5. Which regime benefits home loan borrowers more?
The Old Regime benefits home loan borrowers because it allows interest deductions under Section 24(b).
Download Automatic Income Tax Preparation Software All-in-One in Excel (F.Y. 2025–26) for the Non-Government Employees
Key Features of the Excel-Based Tax Preparation Utility
- Dual Regime Option:
You can effortlessly choose between the New or Old Tax Regime under Section 115BAC. Furthermore, the tool automatically compares both regimes to help you identify the most tax-saving option. - Customised Salary Structure:
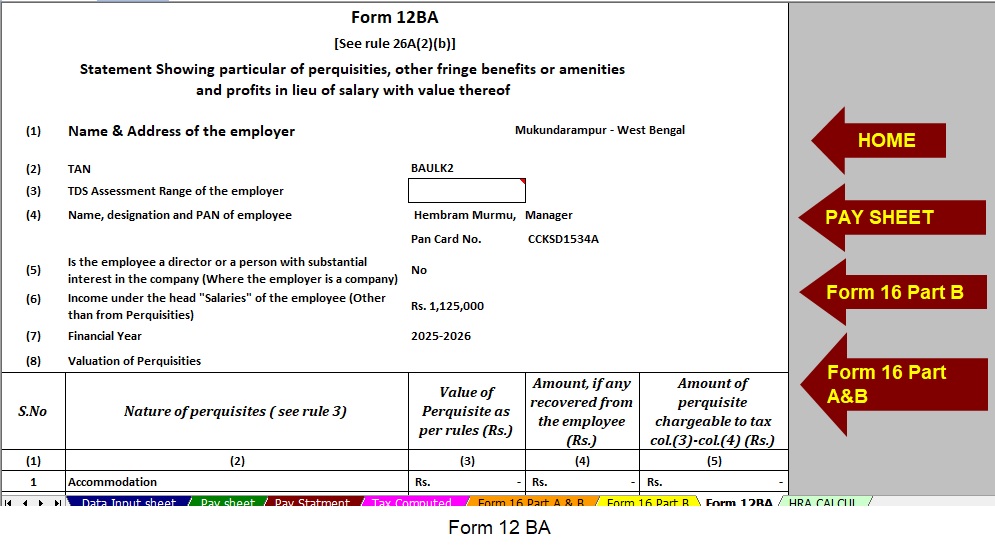
It automatically adjusts according to your salary format, whether you belong to a Non-Government organisation. Additionally, this customisation reduces manual entry and saves valuable time. - Automatic Preparation of the Form 12 BA
- Updated Form 16 (Part A & B) and Part B also
This tool automatically generates Revised Form 16 (Part A & B) and Part B for the Financial Year 2025–26. Likewise, it ensures that your Form 16 remains compliant with the latest tax formats. - Simplified Compliance:
It ensures quick and error-free tax computation through advanced built-in formulas. Furthermore, you can confidently prepare your return with zero manual intervention, enhancing both speed and accuracy.