1. Understanding Salary Arrears
Firstly, salary arrears refer to income that an employee earns in earlier financial years but receives at a later date. For instance, pay revisions, DA arrears, and pending increments commonly fall into this category. Moreover, employers usually release these amounts in one lump sum. As a result, this sudden payment increases total income for the year. Consequently, the taxpayer often moves into a higher tax slab. Therefore, salary arrears directly raise the overall tax burden if no relief is claimed.
2. What Is Relief U/s 89(1)?
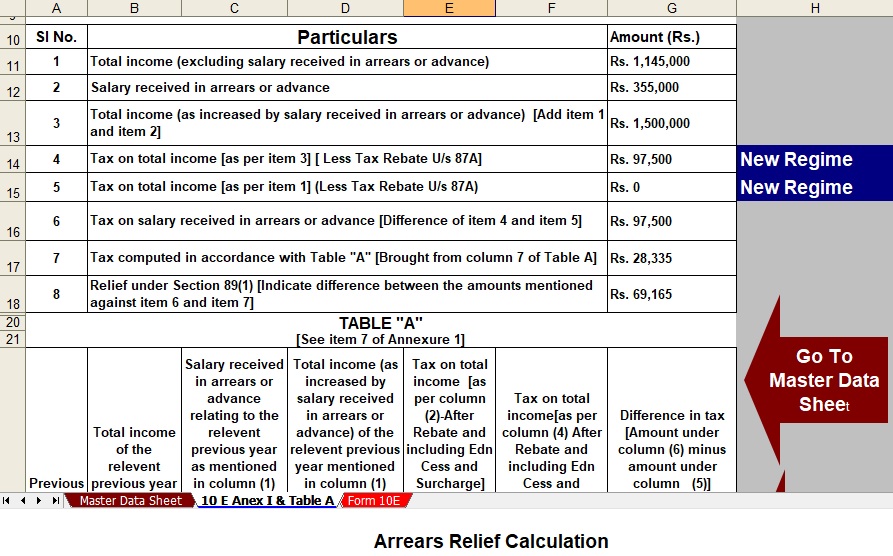
Secondly, relief under Section 89(1) helps taxpayers reduce the additional tax liability created by salary arrears. In simple terms, this provision redistributes the arrears income across the years in which the employee originally earned it. As a result, the tax calculation becomes fair and balanced. Therefore, Section 89(1) prevents taxpayers from paying excess tax merely due to delayed salary payments.
3. Why Salary Arrears Increase Tax
Thirdly, when taxpayers add salary arrears to their current income, the total taxable income rises immediately. Consequently, the applicable tax rate also increases. Moreover, higher slabs lead to higher tax outgo. However, Section 89(1) addresses this issue effectively. Therefore, by applying relief, taxpayers can neutralise the sudden tax impact of arrears.
4. How Section 89(1) Works
Next, Section 89(1) works through a comparison method. Firstly, it calculates tax on total income including arrears. Secondly, it recalculates tax by allocating arrears to the respective past years. Then, it compares both tax amounts. Subsequently, the difference between these two calculations becomes the relief amount. Hence, taxpayers ultimately pay a lower and more accurate tax.
5. What Is an Automatic Relief Calculator
Now, an Automatic Income Tax Salary Arrears Relief Calculator U/s 89(1) functions as a digital solution that performs all calculations instantly. Instead of manual computation, users simply enter income details. Consequently, the calculator processes data quickly. Moreover, it delivers accurate results without confusion. Therefore, it simplifies an otherwise complex calculation process.
6. Benefits of Using an Automatic Calculator
Furthermore, using an automatic calculator offers several advantages. Firstly, it saves valuable time. Secondly, it minimises human error. Additionally, it ensures compliance with income tax rules. Moreover, it delivers instant results. As a result, it works like a personal tax assistant that guides users smoothly through the relief calculation process.
7. Who Can Claim Relief U/s 89(1)
Importantly, any salaried taxpayer who has received salary arrears can claim relief under Section 89(1). Likewise, employees who paid higher tax due to arrears also qualify. Therefore, both government and non-government employees benefit equally. In short, eligibility depends on arrears receipt, not employment type.
8. Role of Form 10E
Equally important, Form 10E plays a critical role in claiming relief. Taxpayers must file Form 10E before claiming Section 89(1) relief. Otherwise, the income tax department may reject the claim. Fortunately, most automatic calculators assist in preparing Form 10E details. Thus, they ensure compliance and accuracy simultaneously.
9. Step-by-Step Working of the Calculator
To begin with, users enter the current year’s income. Next, they input the total arrears amount. Then, they provide income details for the relevant past years. After that, the calculator automatically computes tax. Finally, it displays the relief amount instantly. As a result, the entire process remains smooth, quick, and transparent.
10. Common Mistakes to Avoid
Although the calculator is easy to use, people still make common mistakes. For example, they often forget to file Form 10E. Additionally, they sometimes enter incorrect past income details. Moreover, they may ignore applicable tax slabs. Therefore, taxpayers should carefully verify all inputs before final submission.
11. FY 2025-26 Tax Rules and Relevance
Meanwhile, for FY 2025-26, revised tax slabs and standard deductions apply. Hence, taxpayers must use updated tools for accurate calculations. Consequently, using the latest Automatic Income Tax Salary Arrears Relief Calculator U/s 89(1) becomes essential for correct relief computation.
12. Manual vs Automatic Calculation
On one hand, manual calculation feels slow and tiring, much like counting grains of rice individually. On the other hand, an automatic calculator works like a weighing machine. In contrast, it delivers fast, precise, and reliable results. Therefore, automation clearly wins.
13. How Employers Use This Tool
Currently, many employers rely on automatic calculators to compute TDS accurately. As a result, they deduct correct tax from salaries. Consequently, employees receive proper relief benefits without delay. Thus, automation benefits both employers and employees.
14. Practical Example Explained
For example, suppose you received ₹2,00,000 as salary arrears in FY 2025-26. The calculator allocates this amount to earlier years. Then, it recalculates the tax for each year. Finally, it shows the eligible relief. Therefore, your overall tax liability reduces significantly.
15. Final Thoughts on Tax Relief
Ultimately, the Automatic Income Tax Salary Arrears Relief Calculator U/s 89(1) is not just a tool but a necessity. It simplifies compliance, reduces stress, and ensures tax fairness. Therefore, if you received arrears, using this calculator is undoubtedly the smartest choice.
Conclusion
To conclude, salary arrears do not have to become a tax burden. With proper understanding and the right digital tool, taxpayers can manage arrears confidently. The Automatic Income Tax Salary Arrears Relief Calculator U/s 89(1) empowers individuals to claim lawful relief easily, accurately, and legally.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Section 89(1) relief used for?
Primarily, it helps reduce extra tax arising from salary arrears or advance salary.
Is Form 10E mandatory for claiming relief?
Yes, filing Form 10E is compulsory before claiming Section 89(1) relief.
Can I use the calculator for previous years?
Yes, most calculators support calculations for multiple past financial years.
Is the Automatic Income Tax Salary Arrears Relief Calculator U/s 89(1) accurate?
Yes, provided you enter the correct data, it delivers highly accurate results.
Who should use this calculator?
Any salaried individual who received arrears during FY 2025-26 should use this calculator.